What is Adult Upper Limb Spasticity?
Adult upper limb spasticity may present as tightness and stiffness
in your arm and/or hand. It can be caused by several conditions or neurologic events, including:
Stroke
|
Multiple Sclerosis
|
Traumatic Brain Injury
Cerebral Palsy
|
Spinal Cord Injury

Flexed Elbow

Flexed Wrist

Pronated Forearm

Clenched Fist

Thumb-in-Palm
Adult Upper Limb Spasticity Can Impact Some of Your Everyday Activities Such As:
Dressing | Upper Limb Mobility | Personal Hygiene | Posture
Designed For Purity, XEOMIN Has Only The Ingredients It Needs To Deliver Results
What is XEOMIN?
XEOMIN is an FDA-approved prescription medication that is used to treat adult upper limb spasticity
XEOMIN is a botulinum toxin type A, which may help to increase mobility and movement in your upper limb
It is an injection that is administered in your doctor’s office

I have difficulty getting myself dressed
66-year old Post-stroke patient
Not an actual patient. Individual results may vary.
How Does XEOMIN Work?
XEOMIN works by blocking the signals your nerves send to the muscles in your arm, so that these muscles can relax and not be as tight. This can improve your ability to move those muscles.
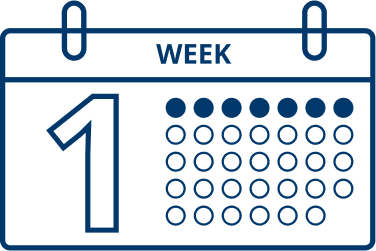
Patients typically start to see results one week after they start treatment with XEOMIN.
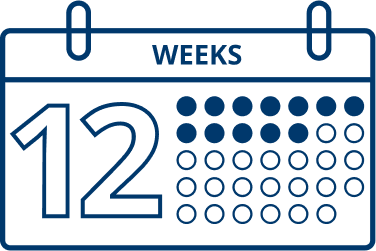
In clinical trials, most patients were retreated after 12 to 14 weeks.
Where is XEOMIN Injected?
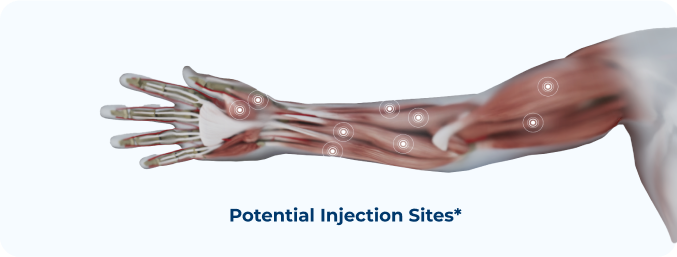
Your doctor will locate certain areas of the upper limb and inject XEOMIN directly into those areas.
If needed, retreatment with XEOMIN can occur every 12 weeks. You and your doctor can decide the right plan for you.
Markings show examples of muscles that may be treated for upper limb spasticity in adults; however, not all possible injection locations are shown. Not all patients will receive treatment in the same muscle(s). Your doctor will will determine the appropriate locations and doses for Xeomin injection.

Not an actual patient.
Individual result may vary.
How Can XEOMIN Help You?
Treatment with XEOMIN may lead to
improvement in muscle tightness or stiffness
Clinical studies with more than 400 patients showed that XEOMIN improved muscle tone and helped with functional improvements.
3 out of 4 patients showed at least minimal improvement in function with XEOMIN and 43% of patients rated their results as much improved or very much improved in function with XEOMIN.
- You’re currently being treated with a neurotoxin
- You’ve had a neurotoxin in the past
- You’re just starting out with a neurotoxin treatment
The Most Common Side Effects in Clinical Trials of XEOMIN in Adults with Adult Upper Limb Spasticity were:
Seizure
|
Nasal Congestion,
Sore Throat and Runny Nose
Dry Mouth
|
Upper Respiratory Infection
Designed For Purity, XEOMIN Has Only The Ingredients It Needs To Deliver Results
XEOMIN is uniquely purified to contain only the therapeutic component. It utilizes XTRACT technology, a state-of-the-art manufacturing process that removes unnecessary proteins.*
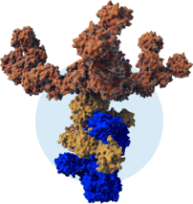
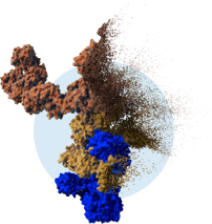
is a state-of-the-art manufacturing process that removes the unnecessary proteins
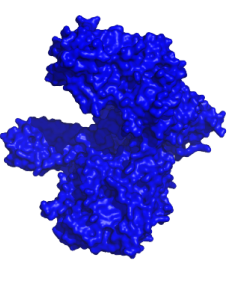
Repeated exposure to neurotoxins with complexing proteins may cause a treatment to not work as well as it once did. XEOMIN does not contain unnecessary proteins that, over time, may increase the risk of losing effectiveness. It is possible with all neurotoxins, including XEOMIN, to lose effectiveness.
†The direct impact of the non-therapeutic proteins on long term safety or efficacy has not been established. Information about the unique XEOMIN manufacturing process and the properties of incobotulinumtoxinA is not intended to imply superiority over other botulinum toxins.
Move Forward with XEOMIN, a Uniquely Purified Option for Adult Upper Limb Spasticity.
The safety and efficacy of XEOMIN has been demonstrated in clinical studies, and XEOMIN has been used in 6.5 million patients with various conditions, from more than 75 countries, for more than 12 years.
Not an actual patient. Individual results may vary.

Patient
Savings Program

Visit MERZCONNECT.com for additional information to help you get started and stay on XEOMIN.
XEOMIN Patient Savings is Available in Just 3 Easy Steps.
Enroll in the program*
Receive XEOMIN treatment
Obtain program savings*†
*Restrictions apply to eligibility. Commercial insurance required.
Reimbursement limited to out-of-pocket XEOMIN medication costs and related administration fees. State limitations may apply. Please see Full Terms and Conditions at MERZCONNECT.com. Merz reserves the right to change XEOMIN Patient Savings Program Terms and Conditions, including the eligibility requirements, at any time. This is not health insurance.
†You may be required to pay upfront for your co-pay/co-insurance, as determined by your insurance coverage/policy and your healthcare provider’s co-pay collection practice.
Once you and your doctor have decided XEOMIN is right for you, MERZ CONNECT offers you savings and support to help you get started and stay on therapy.

