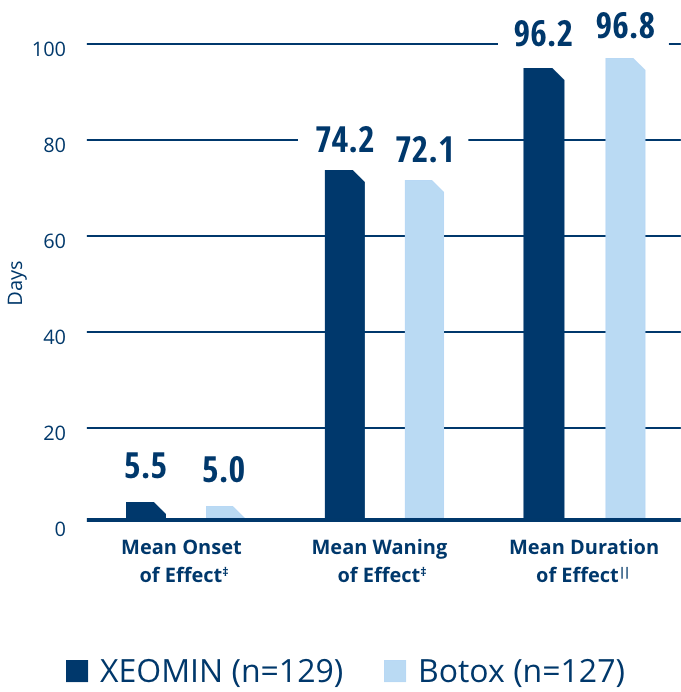
What can waning efficacy look or sound like?
Over time, repeated exposure to neurotoxins with complexing proteins can contribute to a decrease in treatment response.
Waning Efficacy and Neutralizing Antibodies
The clinical relevance of immunogenicity is primarily associated with the development of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), which can lead to secondary non-responsiveness or a waning of clinical effect.
BoNT therapy is often lifelong in patients with chronic conditions; thus, the potential for immunogenicity and risk of reducing NAb production should be considered when making treatment decisions regarding BoNT formulation”1
WATCH IMMUNOLOGIST DR WARNER CARR DISCUSS THE IMPACT OF NAb ON TREATMENT RESPONSE
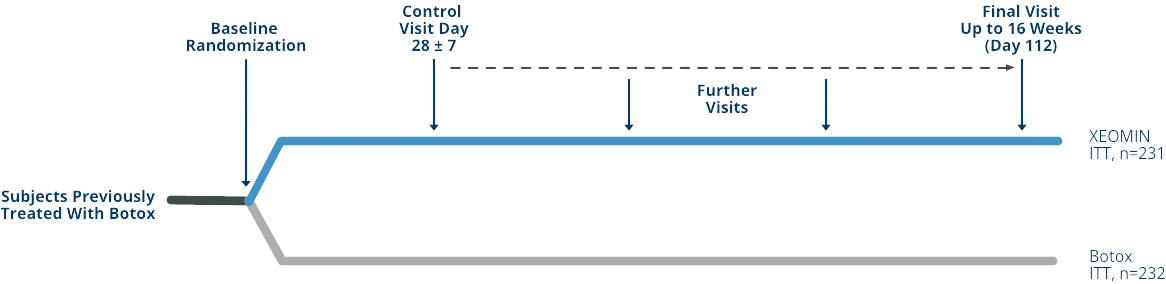
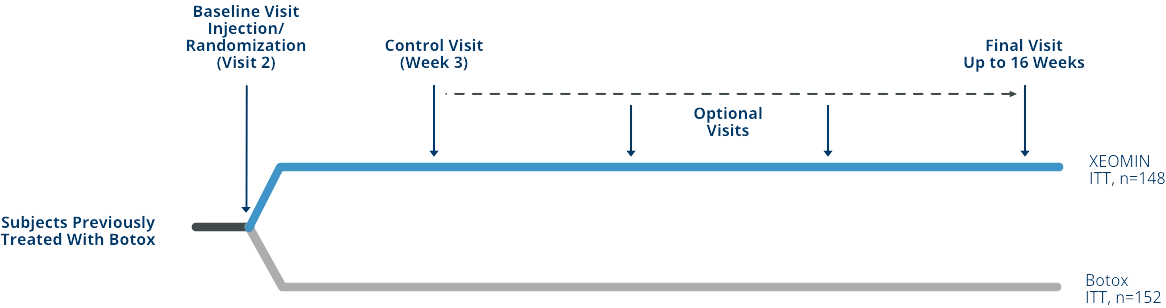
Signs of Waning Efficacy with Chronic, Long-term Exposure to Proteins in Neurotoxin Formulations
NAb formation does not occur in all patients, but because of its increasing likelihood with long-term neurotoxin use, it should be considered when starting or adjusting therapy.1
COMPLEXING PROTEINS MAY CONTRIBUTE TO NAb FORMATION



The direct impact of the non-therapeutic proteins on long-term safety or efficacy continues to be evaluated. Information about the unique XEOMIN manufacturing process and the properties of incobotulinumtoxinA is not intended to imply superiority over other botulinum toxin type A products.
There is a potential for immunogenicity with the use of any botulinum toxin formulation. This information is not meant to imply superiority of safety or efficacy of any toxin; differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies across products or studies. The effect of the presence or absence of antibodies on a product's safety or efficacy continues to be evaluated.
FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; NAbs, neutralizing antibodies.